Yield farming can be a lucrative way to earn passive income in the DeFi space, but many investors find themselves overwhelmed by complex strategies and unexpected risks. The allure of high returns often leads to significant losses due to impermanent loss, volatile markets, and hidden fees. To navigate these challenges and maximize your profits, you need a solid understanding of effective yield farming strategies that balance risk and reward. This guide will show you how.
Introduction to Yield Farming
Definition and Historical Context
Yield farming, also known as liquidity mining, is a method of earning rewards by providing liquidity to decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms. It involves locking up your cryptocurrency in a liquidity pool, a type of smart contract, where it facilitates trading on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) or other DeFi applications. In return, you earn rewards in the form of interest, additional tokens, or fees generated by the platform.
The concept of yield farming emerged in 2020, during the “DeFi Summer,” when platforms like Compound and Uniswap popularized the practice by offering lucrative returns to users willing to provide liquidity. This practice quickly spread across the Ethereum blockchain and beyond, becoming a cornerstone of the DeFi ecosystem. Over time, yield farming has evolved, with more complex strategies and tools being developed to optimize returns.
Importance in the DeFi Ecosystem
Yield farming plays a critical role in the DeFi ecosystem by providing the necessary liquidity that enables decentralized applications to function effectively. By incentivizing users to contribute their assets, yield farming helps to decentralize control, reduce reliance on centralized intermediaries, and increase the overall efficiency and robustness of DeFi platforms.
Moreover, yield farming drives innovation within the DeFi space. It encourages the development of new financial instruments and services, such as automated market makers (AMMs), yield aggregators, and cross-chain farming solutions. These innovations have not only expanded the possibilities within DeFi but also attracted a broader range of participants, from retail investors to institutional players, further accelerating the growth and adoption of decentralized finance.
How Yield Farming Works
Basic Mechanics: Liquidity Pools, Smart Contracts, Tokens
At its core, yield farming involves providing liquidity to decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms in exchange for rewards. The process hinges on three primary components:
- Liquidity Pools: These are smart contracts that hold users' funds to facilitate trading on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) or other DeFi protocols. When you contribute your assets to a liquidity pool, you become a liquidity provider (LP). Your assets enable other users to trade without needing a centralized exchange, and in return, you earn rewards.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automate the process of yield farming, from managing the liquidity pool to calculating and distributing rewards. These contracts ensure that the entire process is transparent, decentralized, and secure.
- Tokens: When you contribute to a liquidity pool, you often receive LP tokens representing your share in the pool. These tokens can be staked or reinvested in other pools to compound your returns. The rewards you earn from yield farming typically come in the form of these tokens, which can be native to the platform or from the broader DeFi ecosystem.
Detailed Explanation of Rewards and Risks
Yield farming offers the potential for high returns, but it also comes with significant risks. Understanding both is crucial for any participant:
- Rewards:
- Interest and Fees: You earn a portion of the fees generated by the protocol, such as trading fees on a DEX. This interest can be quite high compared to traditional financial products.
- Additional Tokens: Many platforms incentivize liquidity providers with additional tokens, often native to the platform (e.g., COMP from Compound). These can be sold for profit or reinvested for compounding gains.
- Risks:
- Impermanent Loss: This occurs when the value of the tokens in the liquidity pool diverges from the value of the same tokens if held outside the pool. The loss is “impermanent” because it only becomes permanent if you withdraw your funds when the divergence exists.
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Although smart contracts automate the process, they are not immune to bugs or exploits. A flaw in the code can lead to significant losses.
- Market Volatility: The value of your staked assets can fluctuate wildly due to the inherent volatility of cryptocurrencies, which can impact your returns negatively.
Step-by-Step Guide to Getting Started (with Visuals)
1. Choose a DeFi Platform and Set Up a Crypto Wallet:
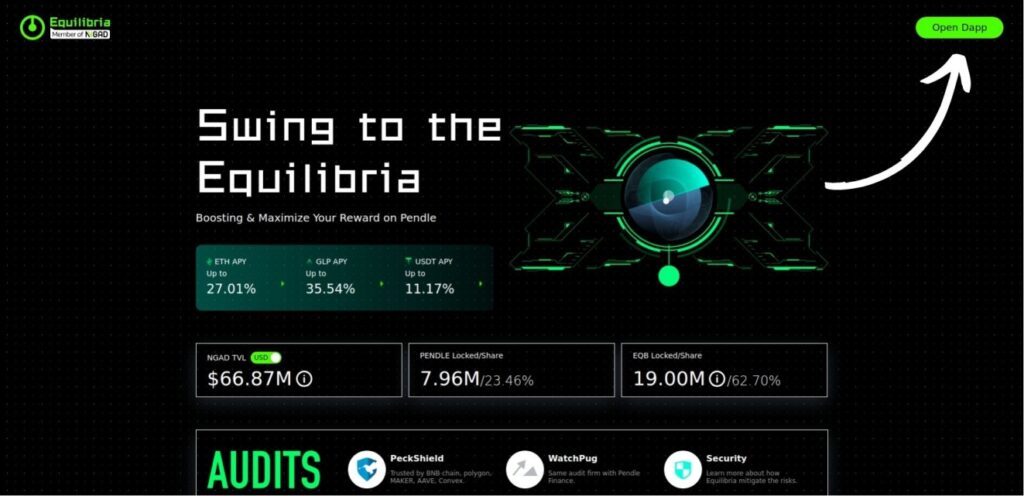
Start by selecting a reputable DeFi platform like Curve or Convex. Consider factors such as Total Value Locked (TVL), user reviews, and the platform’s history to assess its reliability. For this guide, we will use Equilibria, a platform known for optimizing yield farming strategies and providing enhanced rewards for Pendle Finance users.
Once you've chosen your platform, set up a compatible wallet, such as Rabby Wallet, that allows interaction with DeFi protocols. Make sure your wallet is funded with the necessary cryptocurrencies, like ETH for Ethereum-based platforms. For detailed instructions on how to install and configure Rabby Wallet, please refer to our comprehensive guide on installing Rabby Wallet.
3. Connect Your Wallet and Select a Liquidity Pool:
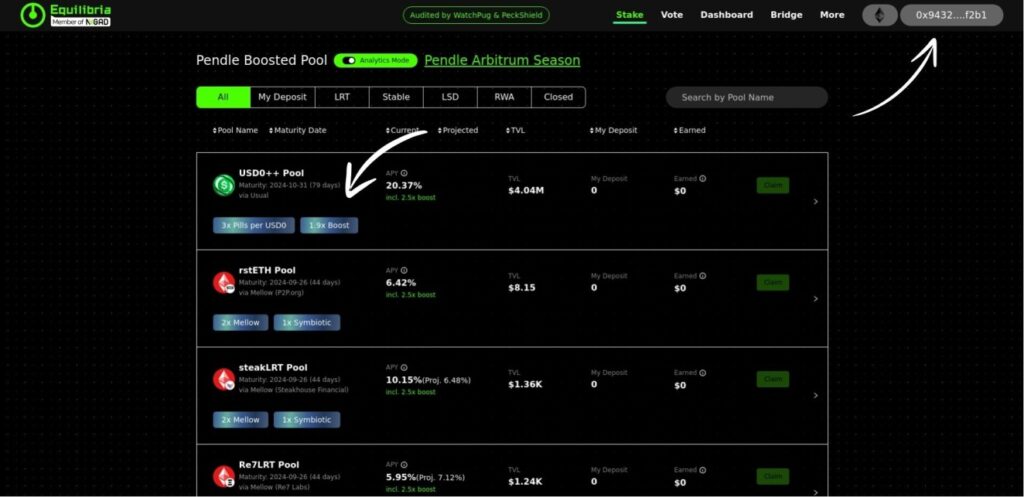
Visit the Equilibria platform and connect your wallet by clicking the “Connect Wallet” button, typically located at the top right of the website. Approve the connection in your wallet interface to proceed. Once connected, you’ll be presented with a variety of liquidity pools.
For this guide, we are choosing the USD0++ Pool as shown in the image above. This pool offers an APY of 20.37% (including a 2.5x boost) and has a Total Value Locked (TVL) of $4.04M. We are selecting this pool specifically to farm Usual pills, which could potentially be eligible for an airdrop in the future.
4. Add Liquidity:
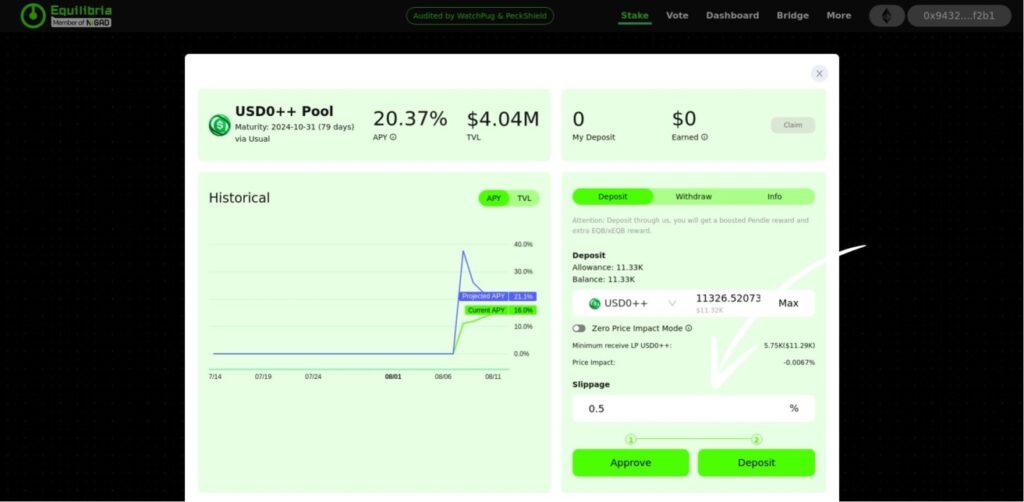
After selecting the USD0++ Pool, it's time to add liquidity. In the “Deposit” section, choose the amount of USD0++ tokens you want to contribute to the pool. The platform will automatically display key details, including your deposit amount, projected APY, and any potential slippage.
To proceed, click on “Approve” to authorize the transaction in your wallet, and then hit “Deposit” to finalize adding your assets to the liquidity pool. The platform will confirm your contribution, and your assets will start earning rewards based on the pool's performance.
5. Monitor Your Investment:
After you've added liquidity, it's crucial to keep track of your investment's performance to stay informed about any potential risks and rewards. You can easily do this by using tools like DeBank or Zapper, which allow you to monitor your DeFi activities across multiple platforms.
To track your investment:
DeBank: Paste your wallet address into DeBank's search bar. This will provide you with an overview of your assets, including the current value of your staked tokens, any accumulated rewards, and your portfolio's overall performance.
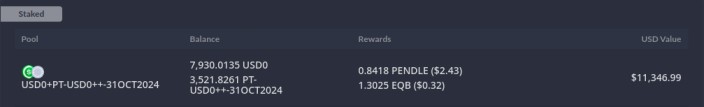
Zapper: Similarly, you can paste your wallet address into Zapper to get a detailed view of your investments. Zapper will show you the balance of your staked tokens, as well as any claimable rewards like PENDLE or other tokens.
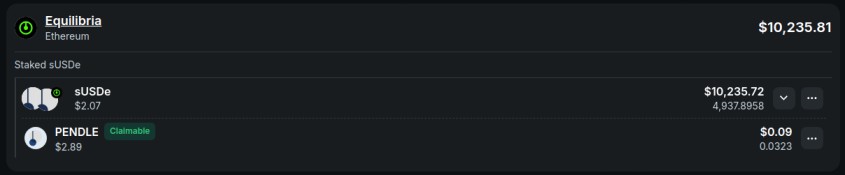
By regularly monitoring your investments using these tools, you can make informed decisions about when to claim rewards, reinvest, or withdraw liquidity based on the performance of your assets and market conditions.
6. Harvest Rewards:
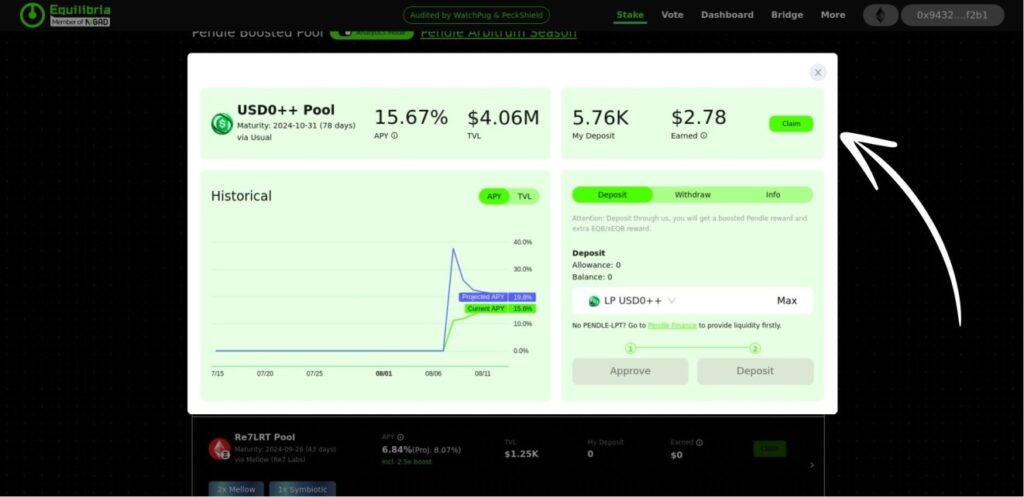
Periodically, you can “harvest” or claim your rewards. This may involve selling the earned tokens or reinvesting them into other pools or strategies for compounding returns.
7. Withdraw Liquidity (if necessary):
If you decide to exit the pool, withdraw your assets through the platform’s interface. Be aware of any fees or penalties that might apply, as well as the potential impact of impermanent loss.
Advanced Yield Farming Strategies
Leveraged Yield Farming
Leveraged yield farming, also known as “looping,” is an advanced strategy that allows you to borrow additional funds to increase the size of your yield farming position. By leveraging, or borrowing, you amplify both potential returns and risks. Here’s how it works:
- Borrowing to Increase Position Size:
- In leveraged yield farming, you use your initial capital to borrow additional assets from a DeFi lending platform. These borrowed assets are then used to provide liquidity, effectively increasing your exposure to yield farming returns. The idea is that the returns from yield farming will exceed the interest costs of the borrowed funds.
- Potential Rewards:
- The main benefit of leveraging is the potential for significantly higher returns. For example, if you borrow twice the amount of your initial investment, your exposure to yield farming rewards is effectively tripled. This can lead to much higher Annual Percentage Yields (APYs) compared to non-leveraged farming.
- Risks:
- However, this strategy comes with high risks. If the value of the assets you’ve borrowed drops, you might face a margin call, where your position is liquidated to cover the loan. Additionally, the interest rates on borrowed funds can fluctuate, potentially reducing your overall profitability.
Leveraged yield farming, or looping, is best suited for experienced investors who understand the risks and have a high tolerance for potential losses.
Cross-Chain Yield Farming
Cross-chain yield farming allows you to take advantage of opportunities across different blockchain networks. As DeFi expands beyond Ethereum, more platforms on networks like Binance Smart Chain, Solana, and Avalanche offer yield farming opportunities. Cross-chain yield farming enables you to:
- Diversify Across Chains:
- By farming across multiple blockchains, you can diversify your investments, reducing the risk associated with any single chain. This diversification can help mitigate issues like high gas fees on Ethereum or network congestion on a particular chain.
- Optimize Yields:
- Different blockchains may offer varying APYs and opportunities. By moving assets between chains, you can optimize your yield farming strategies to always chase the highest returns available. Tools like cross-chain bridges facilitate the transfer of assets between networks, making this process more accessible.
- Risks:
- The main risks include bridge vulnerabilities, where the cross-chain bridge could be compromised, leading to asset loss. Additionally, managing multiple assets across different blockchains can be complex and may involve additional fees and time.
Cross-chain yield farming is ideal for advanced users looking to maximize their returns by exploiting the best opportunities across multiple blockchain ecosystems.
Maximizing Returns through Automation and Yield Aggregators
Automation and the use of yield aggregators are essential strategies for optimizing your yield farming efforts without constant manual intervention.
- Yield Aggregators:
- Yield aggregators, such as Yearn Finance or Harvest Finance, automatically move your assets across different yield farming opportunities to maximize returns. These platforms pool assets from multiple users and allocate them to the most profitable strategies available, including staking, lending, and liquidity provision.
- Benefits of Automation:
- Automation reduces the need for constant monitoring and manual adjustments. By leveraging smart contracts and algorithms, yield aggregators can continuously optimize your positions, moving funds to the highest-yielding opportunities as market conditions change.
- Tools and Platforms:
- Besides aggregators, tools like auto-compounders automatically reinvest your earnings into the same pool, enhancing your returns through the power of compound interest. Examples include PancakeSwap’s auto-compounding pools or Beefy Finance’s vaults.
- Risks:
- While automation simplifies yield farming, it comes with risks such as smart contract vulnerabilities and potential inefficiencies in how funds are reallocated. It's important to choose well-audited platforms and understand the strategies they employ.
Maximizing returns through automation and yield aggregators is particularly useful for those who want to optimize their yield farming returns without dedicating significant time to manual management.
Popular Yield Farming Platforms
Detailed Comparisons of Major Platforms
When it comes to yield farming, a few major platforms stand out due to their reliability, liquidity, and innovative features. Below are detailed comparisons of some of the most popular yield farming platforms:
Uniswap
Overview: Uniswap is a decentralized exchange (DEX) on the Ethereum blockchain that allows users to swap ERC-20 tokens directly from their wallets. It operates using an Automated Market Maker (AMM) model, where users provide liquidity to pools and earn fees from trades.
Key Features:
- Liquidity Pools: Users can contribute to various liquidity pools, earning a share of the 0.3% trading fee distributed proportionally based on their share in the pool.
- Governance: Uniswap has its governance token, UNI, which allows holders to vote on important platform upgrades and changes.
Pros:
- High liquidity and large user base.
- Simple interface and easy integration with Ethereum wallets.
Cons:
- High gas fees on Ethereum can eat into profits.
- Vulnerable to impermanent loss, especially in volatile markets.
Curve Finance
Overview: Curve Finance is a decentralized exchange designed specifically for stablecoins and similar assets. It uses an AMM model optimized for low slippage and low fees, making it ideal for trading stablecoins and pegged assets.
Key Features:
- Liquidity Pools: Curve offers a wide variety of pools where users can deposit stablecoins or other pegged assets and earn trading fees along with rewards in CRV, the platform's governance token.
- Stability and Efficiency: Due to its focus on stablecoins, Curve is known for its efficient trades with minimal slippage.
Pros:
- Low fees and low slippage due to the stablecoin focus.
- Rewards in CRV tokens, which can be further boosted with voting lockups.
Cons:
- Lower yield compared to riskier pools.
- Complex interface that might be challenging for beginners.
Convex Finance
Overview: Convex Finance is a platform built on top of Curve Finance that allows users to boost their CRV rewards without locking up their CRV tokens directly. It pools CRV tokens from various users, voting to maximize rewards and distribute them among participants.
Key Features:
- Boosting Rewards: Convex maximizes rewards from Curve by locking CRV tokens and participating in Curve's governance. It redistributes these boosted rewards to users, who can stake their Curve LP tokens on Convex.
- Integration with Other Protocols: Convex also boosts rewards for other protocols that integrate with Curve, such as Prisma, Frax, and FX protocols, by optimizing their yield farming strategies.
Pros:
- Enhanced returns on Curve LP tokens without the need to directly lock CRV tokens.
- Simple interface for maximizing Curve rewards with minimal effort.
Cons:
- Smart contract risks inherent in using a third-party platform.
- Dependent on the performance and governance of Curve Finance.
New and Emerging Platforms to Watch
As the DeFi ecosystem continues to grow, new platforms are constantly emerging, offering innovative approaches to yield farming. Here are a few to keep an eye on:
Pendle Finance
Overview: Pendle Finance is a permissionless yield-trading protocol that allows users to manage and trade yield from yield-bearing assets. It gained significant attention during the rise of the restaking meta, providing unique opportunities for yield farmers.
Key Features:
- Yield Tokenization: Pendle tokenizes future yield, allowing users to trade it independently from the principal asset. This creates new opportunities for hedging and speculation.
- Restaking Integration: Pendle became popular as it integrated with restaking platforms, allowing users to maximize their returns by participating in multiple yield opportunities simultaneously.
Why Watch: Pendle's innovative approach to yield trading and its integration with the growing restaking meta make it a platform to watch as DeFi continues to evolve.
Equilibria
Overview: Equilibria is a yield optimization platform built specifically for Pendle Finance. Similar to how Convex optimizes rewards for Curve users, Equilibria allows Pendle farmers to boost their rewards without locking up their PENDLE tokens directly. By aggregating PENDLE tokens from multiple users, Equilibria maximizes returns through strategic staking and voting within Pendle’s ecosystem.
Key Features:
- Boosted Rewards: Equilibria enhances the yield farming rewards on Pendle by leveraging the combined voting power of pooled PENDLE tokens.
- Integration with Pendle: The platform is closely tied to Pendle’s ecosystem, providing users with optimized yield opportunities through a streamlined process.
Why Watch: As a dedicated layer on top of Pendle Finance, Equilibria plays a critical role in maximizing returns for Pendle users, making it an essential tool for those deeply involved in Pendle’s yield farming strategies.
Asymmetry Finance
Overview: Asymmetry Finance is a DeFi platform that enhances yield farming within the Curve and Convex ecosystems. Its primary product is a unique CVX (Convex Finance) wrapper designed to offer superior yield optimization. Asymmetry Finance aims to provide more efficient and higher-yielding solutions compared to other CVX wrappers like Clever (clevCVX) and Pirex (pxCVX).
Key Features:
- Advanced CVX Wrapper: The core product of Asymmetry Finance is an advanced CVX wrapper that allows users to stake their CVX tokens and earn higher rewards. This wrapper is designed to optimize returns through innovative strategies that differentiate it from other solutions in the market.
- Integration with Curve and Convex: By leveraging the deep liquidity and established protocols of the Curve and Convex ecosystems, Asymmetry Finance offers a robust platform for users seeking to maximize their yield farming rewards while minimizing risks associated with liquidity and volatility.
- Gem Rush and Potential Airdrop: Asymmetry Finance has introduced “The Gem Rush,” an event where users can potentially earn the platform's native token, $ASF, through active participation. This event is designed to incentivize early adopters and could lead to a lucrative airdrop for participants.
Why Watch: Asymmetry Finance stands out due to its focus on providing better yield optimization for CVX holders. With its advanced CVX wrapper and the potential for rewards through the Gem Rush event, it offers attractive opportunities for those invested in the Curve and Convex ecosystems. The prospect of an airdrop further adds to its appeal, making it a platform worth watching closely.
These platforms highlight the diversity and innovation within the DeFi space, offering different risk-reward profiles and opportunities for yield farmers. By staying informed about both established and emerging platforms, yield farmers can better navigate the dynamic DeFi landscape.
Risk Management in Yield Farming
In-Depth Analysis of Impermanent Loss and How to Mitigate It
Impermanent Loss is one of the most significant risks in yield farming. It occurs when the value of the assets you’ve provided to a liquidity pool changes relative to when you deposited them. This loss is “impermanent” because it only becomes permanent when you withdraw your assets from the liquidity pool. Here’s how it works and ways to mitigate it:
- Understanding Impermanent Loss:
- When you provide liquidity to a pool, you typically deposit two different tokens (e.g., ETH and USDT) in a 50:50 ratio. If one of these tokens appreciates or depreciates significantly, the pool rebalances to maintain this ratio, which can result in a loss compared to simply holding the tokens.
- The loss is considered impermanent because, theoretically, if the token prices return to their original values, the loss is mitigated. However, in volatile markets, this recovery is uncertain.
- Mitigation Strategies:
- Choose Stablecoin Pairs: Providing liquidity in pools that consist of stablecoins (e.g., USDC/DAI) can significantly reduce the risk of impermanent loss because these assets have lower volatility.
- Use Impermanent Loss Calculators: Tools like impermanent loss calculators can help you estimate potential losses before providing liquidity, allowing you to make more informed decisions.
- Diversify Across Pools: By spreading your assets across multiple pools with varying risk levels, you can reduce the impact of impermanent loss on your overall portfolio.
Smart Contract Risks and How to Evaluate Platform Security
Smart Contract Risks arise from the possibility of vulnerabilities or bugs in the code that governs DeFi protocols. Since good smart contracts are immutable once deployed, any flaws can lead to significant financial losses. Here’s how to assess and manage these risks:
- Understanding Smart Contract Risks:
- Exploits and Hacks: Malicious actors can exploit vulnerabilities in smart contracts to drain funds from liquidity pools or manipulate the protocol’s functions.
- Code Bugs: Even well-audited contracts can have bugs that lead to unintended outcomes, such as incorrect reward distributions or locked funds.
- Evaluating Platform Security:
- Audit Reports: Always check if the protocol’s smart contracts have been audited by reputable firms (e.g., CertiK, ConsenSys Diligence). Audits don’t guarantee security but do reduce the likelihood of vulnerabilities.
- Track Record: Consider the platform’s history—platforms that have been operating for longer without incidents tend to be more reliable.
- Bug Bounty Programs: Platforms that offer bug bounties are often more secure, as they incentivize the community to find and report vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them.
- Community and Governance: Active community involvement and decentralized governance can also be indicators of a platform’s reliability, as these factors often lead to more rigorous oversight and quicker responses to potential issues.
Managing Market Risks and Volatility
Market Risks and Volatility in yield farming are inherent due to the fluctuating nature of cryptocurrency prices. Managing these risks is crucial to maintaining profitability:
- Understanding Market Risks:
- Price Volatility: Cryptocurrencies are notoriously volatile, and the value of assets in liquidity pools can swing wildly, affecting both your principal and your returns.
- Liquidity Risks: In less liquid markets, large trades can lead to significant price slippage, impacting the profitability of yield farming.
- Risk Management Strategies:
- Use Stablecoins: Integrating stablecoins into your yield farming strategy can mitigate the impact of market volatility. Stablecoins provide more predictable returns and lower exposure to drastic price changes.
- Monitor Market Conditions: Regularly monitor market conditions and be prepared to adjust your positions in response to significant price movements or changes in market sentiment.
- Diversification: Spread your investments across different protocols, asset types, and blockchain networks to reduce exposure to the risks associated with any single platform or asset.
By understanding and implementing these risk management strategies, you can better navigate the inherent uncertainties of yield farming, maximizing your potential rewards while minimizing your exposure to losses.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Success Stories in Yield Farming
1. Yearn Finance and the Rise of Automated Yield Farming
- Overview: Yearn Finance, founded by Andre Cronje in 2020, became a significant success in the DeFi space by automating the process of yield farming. The platform aggregates liquidity from various protocols and automatically deploys it to the most profitable yield farming opportunities.
- Success Factors:
- Automation: Yearn's Vaults automate the movement of funds between different yield farming strategies, optimizing returns without requiring constant user intervention.
- Community-Driven Development: The platform’s governance token, YFI, allowed the community to participate actively in the platform's evolution, fostering trust and rapid adoption.
- Impressive Returns: Early users of Yearn’s Vaults experienced substantial returns, which propelled the platform’s growth and popularity.
- Impact: Yearn Finance demonstrated the potential of automated yield farming, leading to a proliferation of similar services and establishing a new standard for yield optimization in DeFi.
2. Aave: Yield Farming Through Lending
- Overview: Aave, a decentralized lending protocol, became a key player in yield farming by allowing users to earn interest on their crypto assets through lending. Aave’s innovative features, such as flash loans and credit delegation, attracted a significant user base.
- Success Factors:
- Flexible Lending Options: Aave offers a wide range of assets for lending and borrowing, enabling users to participate in yield farming by earning interest on a variety of cryptocurrencies.
- Security and Reliability: Aave’s robust smart contract audits and transparent governance contributed to its reputation as a secure platform, encouraging more users to lock their assets.
- Growth of DeFi: As DeFi grew, so did the use of Aave, with total value locked (TVL) in the platform increasing exponentially, reaching billions of dollars.
- Impact: Aave’s success in yield farming through lending highlighted the importance of security, flexibility, and innovation in attracting users and growing TVL in DeFi platforms.
Lessons from Yield Farming Failures
1. Iron Finance and the TITAN Collapse
- Overview: Iron Finance, a partially collateralized stablecoin protocol on the Polygon network, faced a catastrophic failure in June 2021 when its native token, TITAN, collapsed from over $60 to near zero in a matter of hours.
- What Went Wrong:
- Over-Leveraging: Users heavily leveraged their positions in TITAN, expecting continued price appreciation, which created a bubble.
- Run on Liquidity: When the price of TITAN began to drop, a panic sell-off ensued, leading to a death spiral where users rushed to withdraw their funds, draining liquidity and crashing the price further.
- Inadequate Mechanisms: The protocol’s mechanisms to stabilize the price of TITAN were insufficient in the face of such a rapid sell-off, leading to its complete collapse.
- Lessons Learned:
- Importance of Robust Price Stabilization Mechanisms: The failure of TITAN emphasized the need for better-designed mechanisms to stabilize token prices, especially in the face of market panic.
- Risk of Over-Leveraging: Yield farmers learned the dangers of excessive leverage, particularly in volatile markets, where a slight downturn can trigger a cascade of liquidations and losses.
2. YAM Finance: A Lesson in Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
- Overview: YAM Finance launched in August 2020 as an experiment in decentralized governance and elastic supply tokens. Within two days of its launch, it gained significant traction but quickly faced a critical failure due to a smart contract bug.
- What Went Wrong:
- Unreviewed Code: The smart contract contained a critical bug in its rebase function, which was not thoroughly tested before deployment.
- Inability to Fix the Issue: The governance system was designed to be decentralized, which made it impossible to quickly implement a fix when the bug was discovered.
- Loss of Funds: As a result of the bug, a large portion of the YAM tokens became irretrievably locked, causing significant financial losses for participants.
- Lessons Learned:
- Importance of Thorough Audits: YAM’s failure highlighted the critical importance of thoroughly auditing smart contracts before deployment, especially in high-stakes DeFi applications.
- Governance and Flexibility: The incident also underscored the need for balance in decentralized governance systems, allowing for emergency interventions when necessary.
These case studies provide valuable insights into the successes and failures in the yield farming space, offering lessons that can help both new and experienced yield farmers navigate the complex and volatile DeFi landscape more effectively.
Future Trends in Yield Farming
The Evolution of DeFi and Yield Farming
Yield farming has evolved rapidly since its inception during the DeFi Summer of 2020. Initially, yield farming primarily involved providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and earning rewards in the form of trading fees or platform-specific tokens. As the DeFi space matured, so did the complexity and variety of yield farming strategies.
- From Simple Liquidity Provision to Complex Strategies: Early yield farming was largely centered around basic liquidity provision. Over time, more sophisticated strategies have emerged, such as leveraged yield farming, cross-chain yield farming, and the use of yield aggregators that automatically optimize returns.
- Integration with Traditional Finance: The line between DeFi and traditional finance (TradFi) is beginning to blur. Institutions are exploring ways to integrate DeFi protocols into their offerings, which could lead to more stability and greater adoption of yield farming as a legitimate investment strategy.
- Sustainability Concerns: As more capital floods into DeFi, the sustainability of high yields is under scrutiny. The evolution of yield farming will likely see a shift towards more sustainable models, possibly with lower, but more consistent, returns.
Upcoming Technologies and Protocols
The next phase of yield farming will likely be driven by innovations in technology and new protocols that address current limitations:
- Layer 2 Solutions: With high gas fees on Ethereum being a significant barrier, Layer 2 solutions like Optimism, Arbitrum, and zk-Rollups are becoming increasingly important. These solutions aim to scale Ethereum by processing transactions off-chain, thereby reducing costs and increasing throughput, making yield farming more accessible and profitable.
- Cross-Chain Interoperability: As more blockchains become viable platforms for DeFi, cross-chain yield farming is gaining traction. Protocols like Polkadot, Cosmos, and Avalanche are enabling seamless asset transfers between different blockchains, allowing yield farmers to chase the best returns across multiple networks without being confined to a single ecosystem.
- Real-World Asset Integration: DeFi protocols are beginning to tokenize real-world assets (RWAs) such as real estate, commodities, and bonds. This trend could lead to yield farming opportunities that are backed by tangible assets, potentially reducing volatility and increasing investor confidence.
- Decentralized Insurance: As the risks associated with yield farming become more apparent, decentralized insurance protocols like Nexus Mutual and Cover Protocol are emerging to offer protection against smart contract failures, hacks, and other risks. This development could make yield farming more attractive to risk-averse investors.
- Decentralized Derivatives DEXes: A new frontier in DeFi is the rise of decentralized derivatives exchanges, which offer innovative models for trading perpetual swaps and options. Platforms like GMX, Aevo, MUX, and Vertex allow users to provide liquidity to derivatives vaults, earning substantial rewards from trading fees and protocol incentives, making them attractive for yield farmers seeking higher returns.
Potential Regulatory Impacts and Their Implications
As DeFi continues to grow, it is increasingly coming under the scrutiny of regulators worldwide. The future of yield farming will be shaped significantly by how the regulatory landscape evolves:
- Increased Regulatory Oversight: Governments and financial regulators are starting to focus on DeFi, particularly regarding anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations. Yield farming protocols may be required to implement stricter compliance measures, which could slow down innovation but also legitimize the space.
- Impact on Decentralization: Regulatory requirements could push some DeFi protocols to become more centralized, especially those that need to comply with KYC and AML rules. This centralization could undermine the core principles of DeFi, such as permissionless access and decentralization, potentially leading to a bifurcation in the ecosystem between fully decentralized and compliant, semi-centralized protocols.
- Global Variability: The regulatory environment for DeFi is likely to vary significantly between different countries and regions. Some jurisdictions may embrace DeFi and yield farming, offering clear guidelines and a favorable environment for innovation, while others may impose stringent regulations or outright bans. This variability could lead to a fragmented global DeFi landscape.
As yield farming continues to evolve, it will be essential for participants to stay informed about these trends and adapt their strategies accordingly. The integration of new technologies and the impact of regulation will play crucial roles in shaping the future opportunities and challenges in yield farming.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Yield farming has emerged as a powerful tool within the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem, offering participants the potential for substantial passive income through a variety of strategies. However, it is not without its challenges and risks. Throughout this guide, we've explored the basic mechanics of yield farming, advanced strategies to maximize returns, popular platforms to consider, and the importance of risk management in this volatile landscape. Key takeaways include:
- Understanding the Basics: Yield farming involves providing liquidity to DeFi platforms, often through liquidity pools, and earning rewards in return. Success requires a solid grasp of how liquidity pools, smart contracts, and tokens work together.
- Advanced Strategies: Leveraged yield farming, cross-chain farming, and the use of yield aggregators can significantly enhance returns but also introduce higher risks, such as liquidation and smart contract vulnerabilities.
- Platform Selection: The choice of platform is crucial. Established platforms like Uniswap, PancakeSwap, and Yearn Finance offer reliability and high liquidity, while emerging platforms present new opportunities but often carry more risk.
- Risk Management: Effective risk management strategies, including mitigating impermanent loss, evaluating smart contract security, and managing market volatility, are essential to protect your investments.
Final Thoughts on the Sustainability of Yield Farming
As yield farming continues to evolve, its sustainability remains a topic of debate. The initial excitement around sky-high returns is giving way to a more mature understanding of the risks and limitations involved. While yield farming offers enticing opportunities, the sustainability of these high yields is questionable, particularly as more participants enter the space and competition for rewards increases.
The future of yield farming will likely see a shift towards more sustainable models, possibly with lower, yet more consistent, returns. The integration of real-world assets, advancements in cross-chain interoperability, and the development of decentralized insurance could play crucial roles in stabilizing the ecosystem. However, regulatory pressures may also shape the trajectory of yield farming, potentially leading to more centralized solutions that align with legal requirements.
In conclusion, yield farming represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector within DeFi. While it offers significant opportunities, it also requires a deep understanding of the associated risks and a strategic approach to participation. By staying informed and adapting to new developments, investors can navigate this complex landscape and potentially reap the rewards that yield farming has to offer.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Common Beginner Questions
1. What is yield farming, and how does it work?
Answer: Yield farming is a process where you earn rewards by providing liquidity to decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms. It typically involves depositing cryptocurrencies into a liquidity pool governed by a smart contract. In return, you receive interest, fees, or platform-specific tokens. The primary goal is to maximize returns by participating in the most lucrative pools or strategies available.
2. How do I start yield farming?
Answer: To start yield farming, you'll need a cryptocurrency wallet (such as Rabby) and some funds (like ETH or stablecoins). Choose a DeFi platform like Uniswap or PancakeSwap, connect your wallet, and select a liquidity pool to provide your assets. Once you've added liquidity, you'll begin earning rewards, which you can later claim or reinvest.
3. What are the risks involved in yield farming?
Answer: Yield farming comes with several risks, including impermanent loss, smart contract vulnerabilities, and market volatility. Impermanent loss occurs when the value of the assets in a liquidity pool diverges from their value if held independently. Smart contract risks involve potential bugs or exploits in the code. Market volatility can lead to significant fluctuations in the value of your assets, impacting your overall returns.
4. How can I avoid impermanent loss?
Answer: While impermanent loss can't be entirely avoided, you can mitigate it by choosing stablecoin pairs for liquidity provision, using impermanent loss calculators, and selecting pools with lower volatility.
5. What are the best platforms for beginners to start yield farming?
Answer: Beginners might find platforms like Uniswap, PancakeSwap, and Aave more user-friendly due to their established reputation, robust security measures, and extensive community support. These platforms also offer a wide range of assets and pools, making it easier to start with lower risks.
Advanced Inquiries and Tips for Experienced Farmers
1. What is leveraged yield farming, and how can I maximize returns using leverage?
Answer: Leveraged yield farming involves borrowing additional assets to increase your position size in a yield farming strategy. This amplifies both potential returns and risks. To maximize returns, experienced farmers can use platforms like Alpha Homora or Alpaca Finance, which allow for leveraged positions. However, it's crucial to monitor your position closely to avoid liquidation and manage the risks associated with volatility.
2. How can I take advantage of cross-chain yield farming opportunities?
Answer: Cross-chain yield farming involves moving assets across different blockchain networks to capitalize on the best yield farming opportunities. Tools like cross-chain bridges (e.g., Matcha, Synapse) facilitate this process, enabling you to transfer assets between networks like Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Avalanche. This strategy allows you to diversify your investments and optimize returns by participating in high-yield pools across multiple ecosystems.
3. What are yield aggregators, and how do they optimize my yield farming strategy?
Answer: Yield aggregators like Yearn Finance and Beefy Finance automatically allocate your assets to the most profitable yield farming strategies available. They pool funds from multiple users and use algorithms to optimize returns, often by moving funds between different pools or platforms. This automation reduces the need for manual management and can lead to higher, more consistent returns by continuously seeking the best opportunities.
4. How can I protect myself from smart contract risks in yield farming?
Answer: To protect against smart contract risks, always choose platforms with a strong track record and those that have undergone rigorous audits by reputable firms. Additionally, consider using decentralized insurance protocols like Nexus Mutual or Cover Protocol, which offer coverage against smart contract failures, hacks, and other risks.
5. What are some emerging trends in yield farming that experienced farmers should watch?
Answer: Experienced yield farmers should keep an eye on the integration of real-world assets (RWAs) into DeFi, the growth of Layer 2 solutions like Optimism and Arbitrum, and advancements in decentralized insurance. These trends are likely to drive the next wave of innovation in yield farming, offering new opportunities to optimize returns and manage risks more effectively.
These FAQs aim to address both common concerns for beginners and advanced strategies for seasoned yield farmers, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the yield farming landscape.


