In the rapidly evolving blockchain space, mastering cross-chain transfers – also known as bridging – is becoming increasingly essential. This comprehensive guide is designed to demystify bridging, helping crypto enthusiasts, DeFi users, and blockchain professionals safely and efficiently move assets across various blockchain networks.
Whether you're new to DeFi, an experienced trader seeking arbitrage opportunities, or a blockchain developer looking to integrate multi-chain solutions, this guide provides the foundational knowledge and practical steps you need.
The Multi-Chain Reality
Today's blockchain landscape is not dominated by a single network but is instead a rich, multi-chain ecosystem. Ethereum remains a leader, yet alternative Layer-1 blockchains like Solana, Avalanche, Binance Smart Chain, and numerous Layer-2 solutions such as Arbitrum and Optimism, have gained substantial traction. Each of these networks offers unique advantages—ranging from lower fees and faster transactions to specialized applications and assets.
However, this diversity creates a challenge: interoperability. Blockchains, by design, are isolated ecosystems unable to communicate or exchange assets directly. Bridging solutions address this fundamental limitation, allowing assets and information to flow seamlessly between chains, unlocking new DeFi opportunities, improved asset utilization, and greater liquidity across the crypto economy.
Key Statistics
The importance of blockchain bridges in today's Web3 ecosystem is clear from recent data:
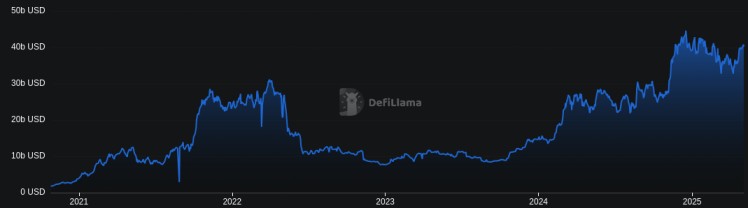
- Total Value Locked (TVL): Over $40 billion in assets are locked within blockchain bridges as of early 2025, underscoring their critical role in the crypto economy.
- Monthly Transaction Volume: Blockchain bridges currently process billions of dollars worth of transactions each month, reflecting their central role in enabling cross-chain activity.
- Web3 Significance: Bridges have become foundational for decentralized finance, enabling cross-chain dApps, decentralized exchanges, lending platforms, and yield strategies to flourish across multiple blockchain environments.
This guide is your roadmap to understanding, selecting, and securely using blockchain bridges to navigate and leverage the multi-chain future.
Understanding Blockchain Bridges: The Foundation
What Are Blockchain Bridges?
Definition and Purpose
Blockchain bridges are systems designed to enable communication and asset transfers between separate blockchain networks. They address the inherent isolation of individual blockchains by creating pathways for tokens, data, and functionalities to move freely between chains. Bridges allow users and applications to leverage the unique strengths and opportunities available on different blockchain platforms.
The Interoperability Problem
Blockchains, by nature, operate independently, without a built-in mechanism to interact with other networks. Each blockchain has its own consensus protocols, security measures, and data formats, making direct communication between them impossible without an intermediary solution. Blockchain bridges effectively solve this problem by creating secure, reliable pathways for interoperability.
Real-World Analogy
Blockchain bridges can be compared to physical bridges that connect islands or separated land areas. Just as physical bridges allow goods, people, and information to flow between isolated regions, blockchain bridges facilitate the secure transfer of digital assets and information between isolated blockchain ecosystems.
How Blockchain Bridges Work
At a high level, blockchain bridges let you move assets or data from one blockchain to another. Since blockchains can't natively talk to each other, bridges act as intermediaries that help assets flow across isolated networks.
Here’s a simplified visual breakdown of how blockchain bridges work – including the two main mechanisms, the components involved, and where things are headed next.
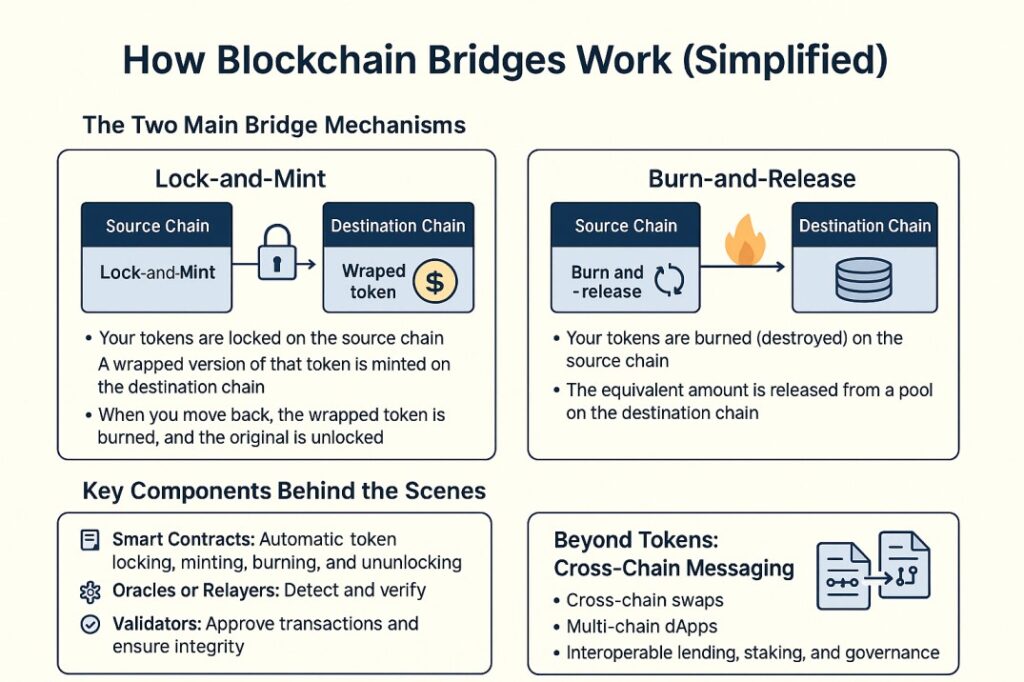
Still Confused? Here's What Actually Matters
You don’t need to understand the full mechanics to bridge safely. Just make sure:
- You’re using a well-known, audited bridge
- The token is supported natively on the destination chain (not a random wrapped version)
- You check the estimated time and fees before confirming
Start small – the rest gets easier with experience.
Why Use a Cross-Chain Bridge?
Bridges aren’t just technical tools – they open up real advantages for everyday crypto users, investors, and builders.
| Financial Benefits | Smarter Portfolio Management | Powering the Multi-Chain Future |
| – Access better yields across DeFi platforms – Move to lower-fee networks – Arbitrage price differences – Combine liquidity across chains | – Diversify across ecosystems – Access exclusive tokens & NFTs – Rebalance without CEXs – Put idle assets to work | – Cross-chain dApps and smart contracts – Combine features from different chains – Offload to scalable Layer 2s – Tap into specialized networks (privacy, storage, gaming) |
Bottom line: Bridges give users freedom, flexibility, and access to a more powerful crypto economy.
Types of Cross-Chain Bridges
While the technology behind cross-chain bridges can get complex, most users only need to understand a few key categories. These help you choose a bridge that fits your needs – whether you want speed, decentralization, or convenience. Ultimately, if you're just moving between chains to access the same native asset (like ETH on Ethereum to ETH on Arbitrum), most reliable bridges will do the job.
Here are the main types of bridges you’ll encounter:
Native or Official Bridges
These are the first bridges launched when a new blockchain ecosystem goes live. They're typically built and maintained by the core development team behind a Layer 1 or Layer 2 – and are considered the most secure and battle-tested entry point into a new chain.
Best used when:
Bridging from Ethereum mainnet into a new ecosystem. They're often the most trusted way to onboard, especially early in a chain's lifecycle.
Caveats:
Withdrawals back to Ethereum can be slower and less user-friendly, sometimes taking hours or days depending on the network.
Examples:
- Arbitrum Bridge (Ethereum ↔ Arbitrum)
- Polygon PoS Bridge (Ethereum ↔ Polygon)
- Hyperliquid Bridge (Ethereum ↔ Hyperliquid)
Best for:
Secure, native-asset transfers from Ethereum into new or official networks – especially when bridging for the first time.
Centralized Bridges (Including Exchanges)
Centralized bridges rely on trusted third parties – like exchanges or custodians – to move assets across chains. You deposit tokens, and the provider handles the transfer by issuing the same token on a different network.
These aren’t technically “bridges” in the on-chain sense, but they’re widely used by everyday crypto users – especially when transferring funds between wallets and Layer 1s or Layer 2s.
Examples include:
- Exchange withdrawals from Binance, Kraken, Coinbase, etc. (e.g., ETH from Ethereum to BNB Chain)
- wBTC – a wrapped Bitcoin issued by custodians like BitGo
- LayerSwap – bridges directly from centralized exchanges to L2s
When it's useful:
- You already have funds on a CEX
- Gas fees are high on-chain and it's cheaper to bridge via withdrawal
- You need speed and convenience over decentralization
Risks to consider:
- You're trusting a third party to hold and release your funds
- Withdrawals can be delayed, blocked, or censored
- If the exchange goes down, your assets may be unrecoverable
- (Not your keys, not your crypto)
Best for:
Users who are already KYC-verified and want a fast, easy way to move funds across chains – but are comfortable trusting centralized platforms.
Liquidity Pool-Based Bridges
Unlike native bridges, which lock and mint assets, these bridges use liquidity pools on each chain to enable direct swaps of assets – often without wrapping. This allows for faster and cheaper transfers, especially when moving between popular chains and tokens.
They're typically governed by their own protocols and tokens, with communities providing liquidity and participating in governance decisions.
When it shines:
- Moving stablecoins like USDC or USDT across chains
- Fast execution with low slippage
- Avoiding wrapped tokens when possible
Examples:
- Stargate Finance – deep stablecoin liquidity across major chains
- Synapse Protocol – supports a wide range of tokens and chains
- Across Protocol – intent-based UX with pooled liquidity, not token wrapping
Best for:
Quick, cost-efficient transfers of native or stable assets across EVM-compatible chains – especially when bridging between Layer 2s or high-volume networks.
Meta Routing and Advanced Bridge Networks
This category includes tools and protocols that go beyond traditional bridging. Rather than relying on a fixed smart contract or static liquidity pool, these platforms optimize, route, or fulfill user intents across multiple chains – sometimes using their own infrastructure, and sometimes aggregating others.
Bridge Aggregators
Bridge aggregators don’t move assets themselves. Instead, they scan multiple bridges and route users to the best path based on fees, speed, and available liquidity.
Examples:
- Jumper Exchange – Aggregates routes across bridges like Synapse, Stargate, Across
- Bungee – Clean interface with swap + bridge in one transaction
Best for:
Users who want the best rate or fastest transfer without researching each bridge manually.
Advanced Protocols (Intent + Messaging)
These protocols fulfill cross-chain intents using their own decentralized infrastructure – often supporting token transfers, messaging, and smart contract calls.
Examples:
- deBridge – Executes token transfers and smart contract messages via its Decentralized Liquidity Network (DLN)
Best for:
Advanced users or developers who want more than bridging – such as composable cross-chain interactions, non-standard token pairs, or flexible routing.
Which One Should You Use?
If you're just moving assets between two major chains (like Ethereum and Arbitrum), it often doesn't matter which type of bridge you use – as long as it’s reliable and supports native assets (not wrapped versions unless necessary).
Where it does matter is if you’re:
- Bridging non-native assets (e.g., USDC or tokens not issued natively on both chains)
- Moving large sums (security and liquidity become more important)
- Seeking the lowest fees or fastest routes (aggregators help)
In the next section, we’ll explore some of the top cross-chain bridges, what they’re best at, and how to use them safely.
The Best Cross-Chain Bridges to Use in 2025
Cross-chain bridging isn’t experimental anymore – it’s infrastructure. What started as a way to move tokens between chains has evolved into a powerful layer for liquidity, composability, and even smart contract execution.
In 2025, the best bridges are fast, affordable, and secure – with some offering far more than just asset transfers. Whether you’re optimizing for fees, yield, speed, or airdrop farming, these are the most trusted and advanced bridge protocols available today.
1. deBridge: Advanced Cross-Chain Infrastructure for the Next Era

deBridge is more than just a bridge – it’s a decentralized interoperability layer designed for token transfers, smart contract calls, and cross-chain messaging. Built for developers and power users, it enables intent-based routing without wrapping tokens or locking liquidity, making it one of the most secure and versatile bridging protocols available today.
What Makes It Different:
Unlike traditional bridges that rely on lock-and-mint models, deBridge does not lock user liquidity. Instead, it uses a Decentralized Liquidity Network (DLN) to fulfill transfers via external liquidity providers, eliminating many of the risks associated with legacy bridging infrastructure.
This model not only improves security but also unlocks faster settlement, support for long-tail tokens, and more composable cross-chain actions.
Key Features:
- DLN fulfillment model (no asset locking or minting)
- Cross-chain messaging and smart contract execution
- Support for niche tokens not found on other bridges
- Available on 23+ chains, including Solana, Sonic, Hyperliquid, and more
Network Performance (as of 2025):
- 1.96 seconds median settlement time
- $10.89 billion in volume settled
- 4 bps lowest spread
- 100% uptime since launch
- 0 security incidents
Supported Chains:
Ethereum, Arbitrum, Optimism, BNB Chain, Polygon, Gnosis, Avalanche, zkSync, Solana, Hyperliquid, Sonic, and others.
Best For:
Advanced users and developers seeking fast, secure, and composable cross-chain transfers – as well as a no-token opportunity for airdrop hunters and points farmers.
Pro Tip:
Use deBridge’s DLN mode to bridge hard-to-find tokens between newer chains. Since it doesn’t lock liquidity, it’s safer and faster – and yes, you can farm points while using it.
👉 Join the deBridge points program via our referral link
2. Stargate Finance
Stargate Finance is a cross-chain bridge built on LayerZero's messaging protocol, enabling seamless native asset transfers across multiple blockchains. It supports over 35 chains, including Ethereum, Arbitrum, Optimism, Polygon, Avalanche, and BNB Chain.
Key Features:
- Instant Guaranteed Finality: Transfers are finalized instantly, ensuring reliability and speed.
- Unified Liquidity Pools: Facilitates efficient capital utilization across chains.
- Economy Mode: Offers gas-efficient transfers by batching transactions, reducing fees.
- Deep Stablecoin Liquidity: Optimized for stablecoin transfers with minimal slippage.
Performance Metrics:
- Total Value Locked (TVL): Approximately $667 million.
- Supported Chains: Over 35, including major Layer 1 and Layer 2 networks.
Use Cases:
- Stablecoin Transfers: Efficiently move stablecoins like USDC and USDT across supported chains.
- Liquidity Provision: Users can provide liquidity to earn fees and STG rewards.
Pro Tip:
For large stablecoin transfers, Stargate often offers the lowest slippage and fastest execution. Utilizing the Economy Mode can further reduce gas fees, making it a cost-effective choice for frequent cross-chain transactions.
3. Across Protocol

Across Protocol is a cross-chain bridge designed to offer rapid, cost-effective, and secure asset transfers across multiple EVM-compatible chains. By leveraging an intent-based architecture, Across allows users to specify desired outcomes, which are then fulfilled by a decentralized network of relayers.
Key Features:
- Ultra-Fast Transfers: Most transactions are completed within seconds, thanks to the protocol's efficient design.
- Decentralized Relayer Network: A robust network of relayers ensures security and reliability in fulfilling user intents.
- No Asset Locking: Unlike some bridges, Across doesn't lock assets in contracts, reducing risk and complexity.
Supported Chains:
Across supports transfers across up to 10 leading EVM-compatible chains, enabling broad interoperability and flexibility for users.
Performance Metrics:
- Total Value Locked (TVL): Approximately $99 million.
Use Cases:
- Stablecoin Transfers: Efficiently move assets like USDC and USDT across supported chains.
- Liquidity Provision: Users can provide liquidity to earn fees and ACX rewards.
Pro Tip:
For users seeking rapid and affordable cross-chain transfers, Across Protocol offers a compelling solution. Its intent-based design simplifies the bridging process, making it accessible even to those new to DeFi.
4. Synapse Protocol
Synapse Protocol is a universal cross-chain liquidity network designed to facilitate seamless asset transfers and communication between various blockchain networks. By leveraging an extensible cross-chain communication protocol, Synapse supports assets, smart contract calls, and more, enabling interoperability across diverse blockchain ecosystems.
Key Features:
- Broad Chain Support: Synapse connects a wide array of blockchains, including both EVM and non-EVM chains, enhancing its versatility.
- Efficient Liquidity Pools: Utilizes Automated Market Maker (AMM) models for efficient asset swaps with minimal slippage.
- Cross-Chain Messaging: Supports generalized cross-chain messaging, allowing for complex interactions beyond simple token transfers.
- Security Measures: Employs multi-party computation (MPC) validators with threshold signature schemes (TSS) to ensure secure and reliable transactions.
Supported Chains:
Synapse supports a diverse range of blockchains, including:
Performance Metrics:
- Total Value Locked (TVL): Approximately $48.56 million.
Use Cases:
- Stablecoin Transfers: Efficiently move stablecoins like USDC and USDT across supported chains.
- Liquidity Provision: Users can provide liquidity to earn fees and SYN rewards.
Pro Tip:
For users seeking a versatile and secure cross-chain bridging solution, Synapse Protocol offers a robust platform with extensive chain support and efficient asset transfer capabilities.
Bridge Aggregators: Let the Tools Choose the Best Route for You
Not sure which bridge to use? You're not alone – with dozens of options and constantly changing fees, it can be hard to know the most efficient path.
That’s where bridge aggregators come in. These platforms scan multiple bridges in real time and automatically route your transfer through the fastest, cheapest, or most reliable option – all through a single interface.
Whether you’re bridging for the first time or just want to avoid decision fatigue, aggregators are the easiest way to get from Chain A to Chain B without worrying about the details.
Jumper Exchange: Your One-Stop Cross-Chain Aggregator
Jumper Exchange, developed by LI.FI, is a comprehensive cross-chain aggregator that simplifies the process of swapping and bridging assets across multiple blockchains. By integrating various bridges and decentralized exchanges (DEXs), Jumper provides users with the most efficient routes for their transactions.
Key Features:
- Extensive Network Support: Connects to over 25 blockchains, including Ethereum, Arbitrum, Polygon, Avalanche, BNB Chain, and more.
- Gas Fee Optimization: Features like LI.Fuel allow users to obtain necessary gas tokens on destination chains, ensuring smooth transactions.
- Real-Time Analytics: Provides detailed information on transaction times, fees, and routes, enabling informed decision-making.
Supported Chains:
Ethereum, Arbitrum, Optimism, Polygon, Avalanche, BNB Chain, Base, zkSync, Linea, Scroll, and more.
Best For:
Users seeking a hassle-free solution for cross-chain transactions, especially when uncertain about the best bridge or DEX to use.
Bungee: Streamlined Cross-Chain Swaps with Smart Routing
Bungee is a bridge aggregator developed by Socket, designed to simplify and optimize cross-chain asset transfers. By aggregating multiple bridges and decentralized exchanges (DEXs), Bungee provides users with the most efficient routes for their transactions.
Key Features:
- Extensive Network Support: Bungee connects over 20 blockchains, including Ethereum, Arbitrum, Optimism, Polygon, Avalanche, BNB Chain, and more.
- Bridge and DEX Integration: Aggregates various bridges and DEXs to find optimal transaction paths.
- Gas Fee Optimization: Features like “Refuel” allow users to obtain necessary gas tokens on destination chains, ensuring smooth transactions.
Supported Chains:
Ethereum, Arbitrum, Optimism, Polygon, Avalanche, BNB Chain, Base, zkSync, Linea, Scroll, and more.
Best For:
Users seeking a hassle-free solution for cross-chain transactions, especially when uncertain about the best bridge or DEX to use.
Quick Comparison: Top Cross-Chain Bridges in 2025
| Bridge | Best For | Supported Chains | Key Features | Pro Tip |
| deBridge | Advanced users, devs, tokenless farming | 23+ incl. Ethereum, Solana, Hyperliquid, Optimism | DLN routing, smart contract calls, no token, niche asset support | Use DLN to bridge niche tokens and farm points securely |
| Stargate | Stablecoin transfers, large volumes | 35+ incl. Ethereum, Arbitrum, Avalanche, BNB, Optimism | Deep stablecoin liquidity, LayerZero finality, gas-efficient Economy mode | Ideal for USDC/USDT moves with low slippage |
| Across | Fast, low-cost transfers of common assets | Ethereum, Arbitrum, Optimism, Polygon, Base, zkSync | Intent-based UX, instant transfers, low fees, no asset locking | Great for ETH/USDC/USDT between L2s — ultra fast |
| Synapse | Bridging non-native or long-tail tokens | 20+ incl. BNB, Arbitrum, Polygon, Avalanche, Base | Liquidity pools, cross-chain messaging, broad asset support | Best for tokens not native on destination chain |
| Jumper | Comparing best bridge routes | 45 chains, 21 bridges, 15 DEXs | Aggregator, fee/gas comparison, token swaps | Use if unsure which route is best |
| Bungee | Beginners seeking a smooth experience | 20+ incl. Arbitrum, Optimism, Base, Ethereum | One-click UI, bridge + swap, fee previews, refuel gas support | Best for users new to cross-chain actions |
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Right Bridge
There’s no one-size-fits-all bridge – and that’s a good thing. Each protocol serves a different type of user or use case. Here's a quick reference guide to help you decide:
| If you want… | Try… |
| Fastest transfer of ETH or USDC | Across |
| Large stablecoin transfers between L2s | Stargate |
| Bridging non-native tokens like USDC.e | Synapse |
| Composable cross-chain actions or niche tokens | deBridge |
| Solana ↔ EVM or NFT bridging | Portal |
| Direct from exchange to Layer 2 | LayerSwap |
| You’re not sure or want optimal routing | Jumper or Bungee |
Tip: Most users benefit from bookmarking 2-3 solid bridges and getting familiar with their flows. Flexibility is key – fees, speeds, and routes change daily in DeFi.
Step-by-Step Guide: Performing a Cross-Chain Transfer with deBridge
In this example, we’ll walk through a real cross-chain transfer using deBridge, one of the most secure and advanced bridges available today.
We'll be sending USDC from Arbitrum to USDC on Gnosis Chain — a common route when preparing to convert into EURe for use with non-custodial crypto debit cards like Gnosis Pay.
This guide is fully illustrated and ideal whether you're bridging for the first time or just want to see how deBridge’s interface works step-by-step.
Preparation: What You Need
Before starting, make sure you have:
- A Web3-compatible wallet like MetaMask or Rabby.
- → Need help? Read our Rabby setup guide
- Sufficient gas fees on the source chain (e.g., ETH on Arbitrum).
- A supported token to bridge (in this example, we'll use USDC).
Execution: How to Bridge Using deBridge
We're bridging USDC from Arbitrum to Gnosis Chain.
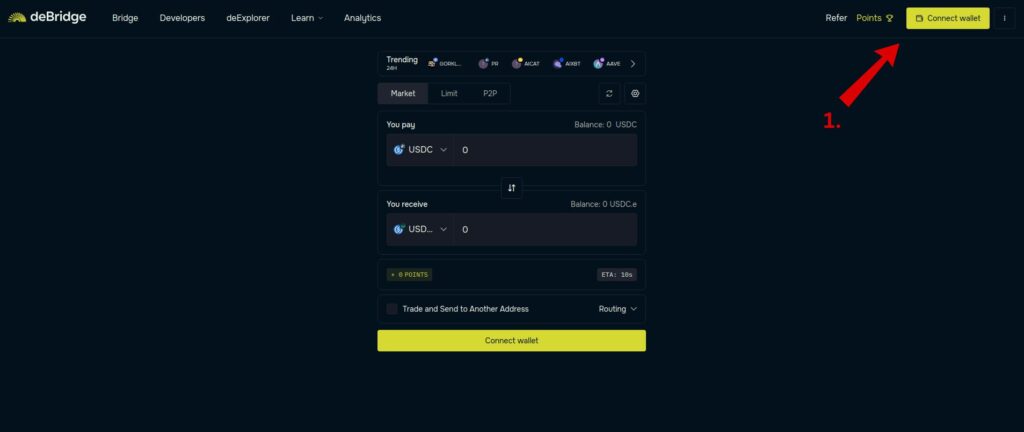
Step 1 – Connect Your Wallet
Go to debridge.finance and click “Connect Wallet” at the top right.
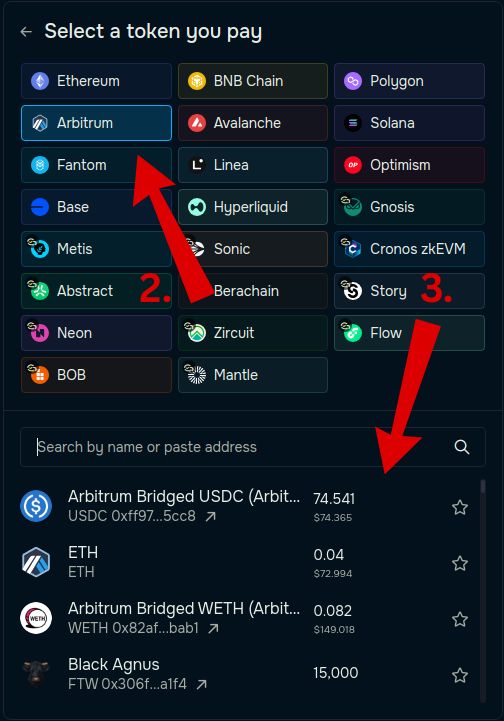
Step 2 – Select Your Source Chain
Click the “You Pay” section and choose the source chain (e.g., Arbitrum).
Step 3 – Select the Token You Want to Send
From the same menu, choose the token you want to bridge (e.g., USDC on Arbitrum).
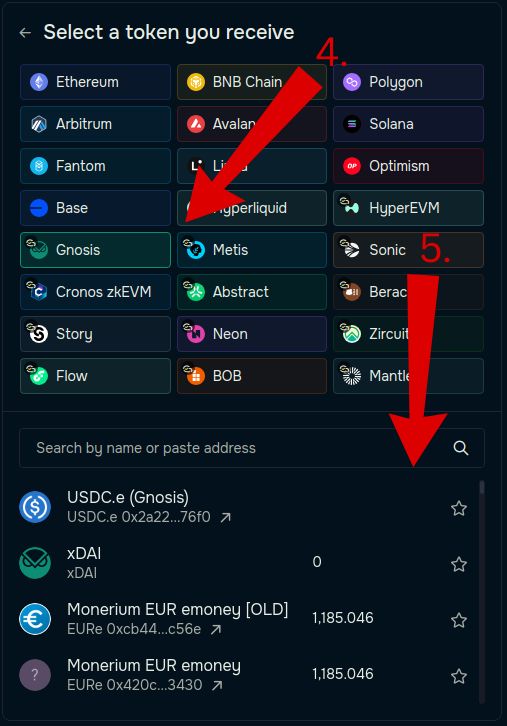
Step 4 – Choose the Destination Chain
In the “You Receive” section, select Gnosis Chain as the destination.
Step 5 – Choose the Destination Token
Choose the token you want to receive on the destination chain (e.g., USDC.e on Gnosis).
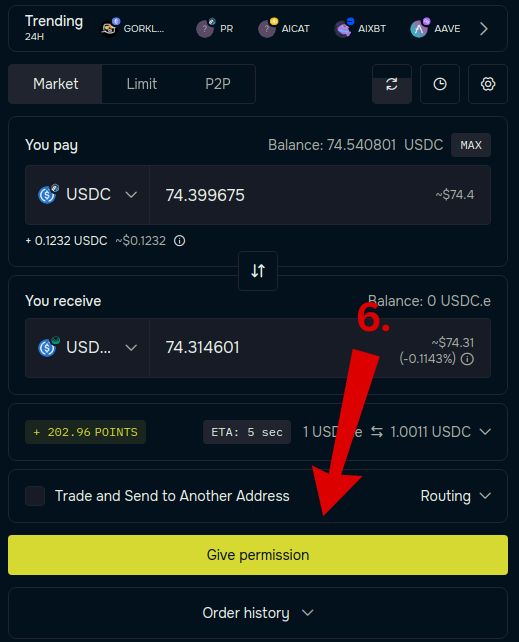
Step 6 – Give Permission
Click “Give Permission” to allow deBridge to use your token. Approve the transaction in your wallet.
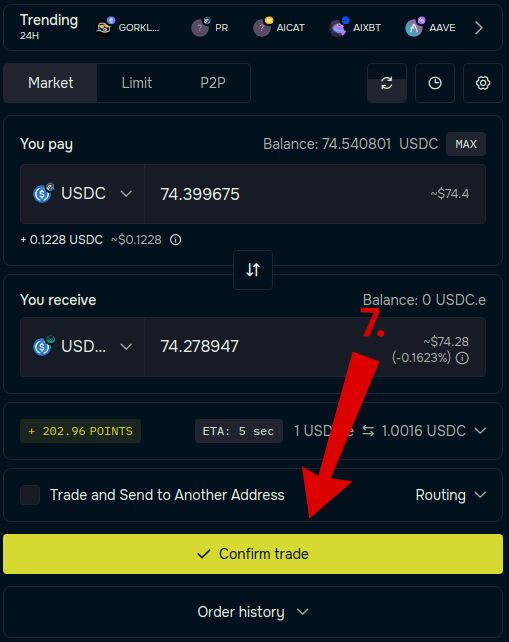
Step 7 – Confirm the Transfer
Click “Confirm Trade” and approve the transaction in your wallet.
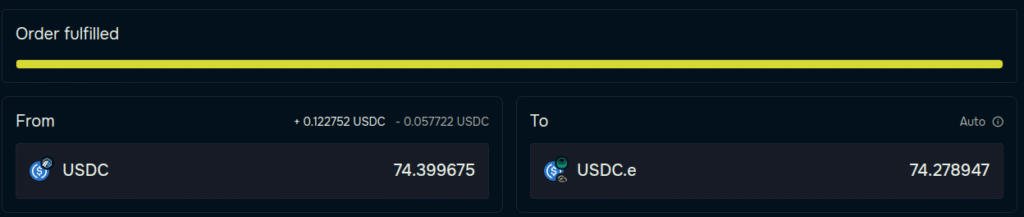
Post-Transfer: Verify and Confirm
- Switch to the destination chain (e.g., Gnosis) in your wallet.
- You should see the bridged token in your balance.
- If not:
- Use block explorers to verify receipt.
- Manually add the token contract if needed.
- Check your Order History on deBridge to view fulfilled transfers.
Pro Tip: Always test with a small transfer first – it reduces risk and gives you confidence before moving larger amounts.
Real-World Use Cases for Cross-Chain Bridges
Cross-chain bridges aren’t just infrastructure – they’re what make crypto actually usable across ecosystems. Whether you're a DeFi user, builder, gamer, or business, bridges unlock access, utility, and efficiency across networks.
| 🪙 DeFi: Chasing Yield Across Chains | 🖼️ NFTs: Expanding Access & Utility |
|---|---|
| Access yields on new chains like Arbitrum, Optimism, or Base. Example: Bridge USDC to Arbitrum for GMX or Uniswap v3. | Bridge NFTs for cheaper gas and new marketplaces. Example: Move NFTs from Ethereum to Polygon for Magic Eden. |
| 🎮 Gaming: Moving Assets Between Worlds | 🏢 Enterprise: Multi-Chain Business Operations |
|---|---|
| Transfer in-game tokens between ecosystems. Example: Bridge game assets from Avalanche to Immutable or Ronin. | Manage assets or activity across L1/L2 stacks. Example: Use Base or Optimism for daily ops from an Ethereum-based dApp. |
Up next: Before you jump in with large transfers or complex setups, let’s review what you need to know to stay safe when using bridges.
Staying Safe When Using Bridges
While bridges unlock powerful opportunities, they’re also some of the most targeted infrastructure in crypto. A little caution goes a long way – here’s how to stay safe.
Common Bridge Risks (What Can Go Wrong)
- Compromised Wallets or Keys:
- Some bridges rely on multi-signature wallets or custodians. If even a few keys are hacked or stolen, funds can be drained.
- Smart Contract Bugs:
- If there’s a flaw in the bridge code, attackers can exploit it to mint tokens, drain liquidity, or halt transfers.
- Oracle or Validator Failures:
- Bridges often rely on validators or oracles to report activity across chains. If those sources are faulty or manipulated, funds can be moved incorrectly or maliciously.
Major Historical Hacks:
- Ronin (2022): $600M lost via validator key compromise
- Wormhole (2022): $325M drained from a smart contract exploit
- Multichain (2023): Ongoing failures due to internal key mismanagement
Bridge Safety Tips for Users
✅ Before You Use a Bridge:
- Check if it has recent audits from trusted security firms
- Look into how it’s secured (is it decentralized or controlled by a few?)
- Choose bridges with high usage and reputation
- Avoid new or unaudited bridges with low TVL (total value locked)
🚩 Red Flags:
- No audit or security information available
- Unclear who runs or verifies the bridge
- Random popups or phishing-like websites pretending to be a bridge
- UI errors or suspicious wallet permissions
💡 Smart Usage Tips:
- Start small — test a small transfer before sending large amounts
- Split big transfers into smaller chunks
- Bookmark the official bridge site to avoid phishing
- Follow bridge teams on Twitter/Discord for alerts and updates
Bridges are powerful, but not without risk. Taking a few precautions can go a long way toward protecting your funds.
Want a deeper dive into protecting yourself in DeFi?
👉 Check out our full DeFi Scam Protection Playbook – packed with real-world examples and defense tactics.
DeFi has come a long way from its early days. What once felt like a risky experiment is now part of everyday user flow – especially when it comes to bridging.
Today, there are dozens of ways to move assets across chains. As a result, most experienced users no longer ask “Which bridge should I use?” – they ask “What’s the most efficient way to get this done?”
That’s the beauty of modern cross-chain infrastructure: it’s becoming invisible. Bridges, aggregators, and even cross-chain swaps now work quietly in the background, letting users focus on outcomes – not logistics.
But that convenience comes with responsibility:
Use trusted tools. Start small. Stay informed.
Bridges are no longer just infrastructure – they’re your passport to the multi-chain economy. Whether you're trading, yield farming, gaming, or building, knowing how to move across ecosystems is essential.
Now that you know how bridges work, which tools to trust, and how to stay safe – you're ready to explore the cross-chain world with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is bridging the same as swapping?
No. Swapping means exchanging one token for another on the same chain (like ETH for USDC). Bridging means moving the same token across different blockchains (like ETH on Ethereum → ETH on Arbitrum).
What is the safest bridge to use?
There’s no perfect answer – but well-audited, widely-used bridges like Across, Stargate, or Synapse are considered secure by many in the DeFi community. Always check for recent audits and usage volume.
Can I lose my tokens when bridging?
It’s rare, but yes – smart contract bugs, phishing, or bridge exploits can result in loss. Always:
-Double-check URLs
-Test with small amounts first
-Avoid new, unaudited bridges
How much does bridging cost?
Costs vary by network and bridge:
–Gas fees depend on the source chain
-Some bridges charge small protocol fees (e.g., $0.01–$1+)
-Aggregators (like Jumper or Bungee) help you find the cheapest route
How long does it take to bridge?
-Fast bridges like Across: ~30 seconds
-Liquidity pool bridges like Synapse: ~1-5 minutes
-Native bridges or congestion: up to 30+ minutes
Always check estimated time on the platform before confirming.
Why do I sometimes get a “wrapped” version of my token?
Some bridges use the lock-and-mint model, where the token is locked on one chain and a wrapped version is created on the other. It’s normal – and you can usually bridge back to get the original.
Is bridging from a CEX (like Binance) the same as using a bridge?
Not quite. CEXs offer centralized bridging during withdrawal – it's simple but requires trust in the exchange. For full control and transparency, use on-chain bridges via a self-custody wallet.
Can I bridge from my mobile wallet?
Yes – many bridges support mobile wallets like Trust Wallet, Rabby, or Coinbase Wallet. Just make sure your wallet supports the source/destination chains and you have gas tokens.


